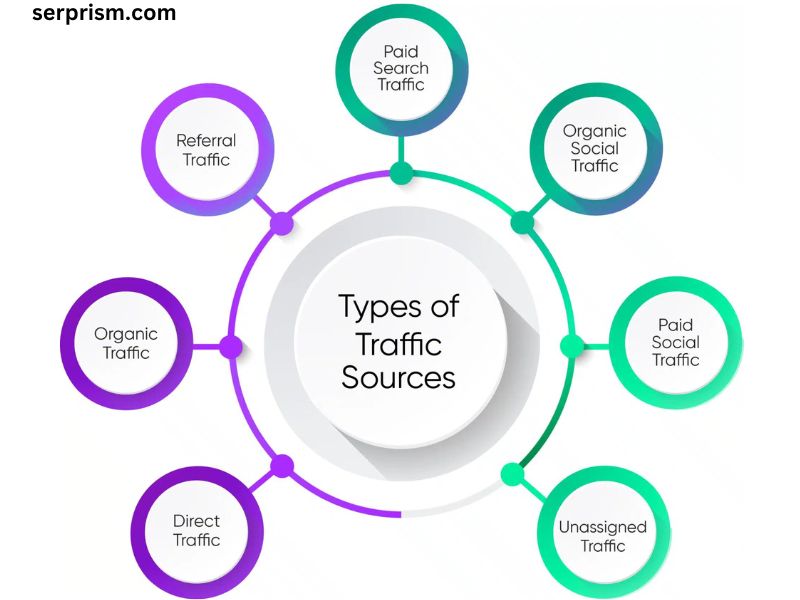
When analyzing website performance through Google Analytics, you’ll often encounter various traffic sources that help you understand how visitors are finding your site. Among these sources, “Direct Traffic” and “Unassigned Traffic” are two categories that can sometimes confuse marketers and web analysts. Understanding the nuances between these two types of traffic is crucial for accurate reporting, optimization, and strategizing your marketing efforts.
What is Direct Traffic?
Direct Traffic refers to visitors who arrive at your website by typing your URL directly into their browser, clicking on a bookmark, or clicking on a link from an untagged email or document. In other words, these are users who have a clear intention to visit your site.
Characteristics of Direct Traffic
- Intentional Visits: Direct traffic typically indicates that users are familiar with your brand or website. They know what they are looking for, which can be a positive sign of brand loyalty.
- Measurement: Google Analytics attributes this traffic to “Direct” if it cannot determine the referrer. This happens in several scenarios:
- A user types your URL directly into the address bar.
- A user clicks on a bookmark.
- Traffic from non-web documents (like PDFs) without proper tagging.
- Some mobile applications and email clients may not pass referrer information.
- Impact on Analytics: High direct traffic can signal a healthy level of brand recognition, but it can also be misleading if not contextualized with other data. For instance, if direct traffic spikes unexpectedly, it may require deeper investigation to identify the cause.
Benefits of Analyzing Direct Traffic
- Brand Awareness: A growing direct traffic segment often reflects effective marketing campaigns, word-of-mouth referrals, or a strong brand presence.
- Engagement Insights: Direct visitors often have lower bounce rates and higher engagement metrics, as they usually come with intent.
- Benchmarking: Monitoring direct traffic over time helps you benchmark your brand’s growth and marketing effectiveness.
What is Unassigned Traffic?
Unassigned Traffic is a broader category that can be more complex to interpret. This label typically appears in Google Analytics when the source of the traffic cannot be identified, meaning it does not fall into the clear categories of direct, organic, referral, or paid traffic.
Characteristics of Unassigned Traffic
- Lack of Referrer Information: Unassigned traffic usually indicates that Google Analytics could not attribute the traffic to any identifiable source, which can occur for various reasons:
- URL shorteners that don’t pass referral data.
- Traffic from HTTPS to HTTP sites where referrer information is stripped.
- Some browsers and privacy settings prevent referrer data from being shared.
- Users clicking on links in non-standard environments, like desktop email applications or apps that do not pass referrer information.
- Ambiguity in Tracking: Unlike direct traffic, unassigned traffic often requires deeper investigation to discern its true origin. It can represent a mix of traffic that is not easily categorized.
- Potential Misleading Data: Because unassigned traffic can contain elements of direct traffic, it can sometimes lead to misconceptions about your website’s traffic sources. For example, an increase in unassigned traffic could indicate issues in tracking or a shift in user behavior.
Implications of Unassigned Traffic
- Tracking Challenges: Since unassigned traffic is ambiguous, it complicates your ability to accurately measure the effectiveness of specific marketing campaigns.
- Conversion Analysis: If a significant portion of your traffic is unassigned, it can affect your conversion rate analysis, as you may not fully understand where your visitors are coming from.
Key Differences Between Direct Traffic and Unassigned Traffic
Attribution
- Direct Traffic: Clearly attributed to visitors who intentionally enter your URL, bookmark your site, or click on links in documents that do not pass referrer information.
- Unassigned Traffic: Lacks clear attribution and can represent a mix of different user behaviors and sources, making it harder to analyze.
User Intent
- Direct Traffic: Indicates a level of brand recognition and intent, as these users are typically familiar with your site.
- Unassigned Traffic: Represents uncertainty regarding user intent, as it includes traffic that may not have a clear path to your website.
Measurement
- Direct Traffic: Easier to measure and analyze over time to gauge brand awareness and user engagement.
- Unassigned Traffic: More complex to interpret; often requires further investigation to discern its origins and implications.
Best Practices for Analyzing and Managing Traffic Sources
Use UTM Parameters
To mitigate unassigned traffic, implement UTM parameters in your marketing campaigns. These tags help define where your traffic comes from, allowing Google Analytics to attribute visits more accurately. Ensure all your links in emails, social media posts, and digital ads are tagged appropriately.
Regularly Audit Your Analytics
Conduct regular audits of your Google Analytics data to identify patterns in your traffic sources. Look for spikes or anomalies in direct or unassigned traffic, and analyze other metrics like user behavior and conversion rates to provide context.
Enhance Brand Recognition
If you notice a growing trend in direct traffic, consider ways to further enhance brand recognition. This could involve investing in content marketing, social media, and SEO to strengthen your online presence.
Explore Traffic Quality
Not all traffic is created equal. Use metrics such as bounce rate, pages per session, and conversion rates to assess the quality of both direct and unassigned traffic. Higher quality traffic typically indicates successful marketing strategies.
Consider Privacy Impacts
Be aware that changes in privacy regulations and browser policies can affect how traffic is categorized. Browsers may block referrer information, leading to increases in unassigned traffic. Staying informed about these changes can help you adapt your tracking and reporting strategies.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between direct traffic and unassigned traffic in Google Analytics is crucial for marketers aiming to optimize their online presence. While direct traffic can reflect brand loyalty and awareness, unassigned traffic poses challenges in attribution and analysis. By employing best practices, such as using UTM parameters and regularly auditing your analytics, you can gain clearer insights into your website’s performance.
In the ever-evolving landscape of digital marketing, leveraging these insights will enable you to make informed decisions, adjust your strategies, and ultimately drive more meaningful engagement with your audience. By navigating the complexities of traffic sources, you can turn data into actionable insights that enhance your online strategy and business outcomes.